Kidney Fibrosis
Kidney Fibrosis
Renal fibrosis is a progressive process resulting from a sustained injury that may ultimately cause renal failure. Impaired renal repair after acute kidney injury induces fibrosis which may ultimately lead to the development of chronic kidney disease.
Signaling Pathway:
Fibrosis is a reactive process that develops in response to excessive epithelial injury and inflammation, leading to myofibroblast activation and an accumulation of extracellular matrix. Developmental signaling pathways - Notch, Wnt and Hedgehog (Hh) - are reactivated in response to kidney injury and contribute to the fibrotic response.
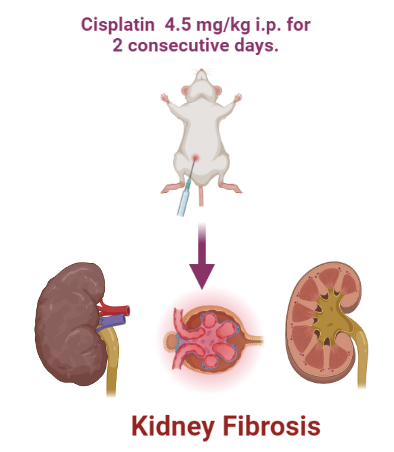
Induction of Kidney Fibrosis:
Cisplatin in saline (0.9 % NaCl (w/v) solution) 4.5 mg/kg i.p. for 2 consecutive days.