Extraction, Isolation and Characterization of Bioactive Natural Compounds
Extraction, Isolation and Characterization of Bioactive Natural Compounds
|
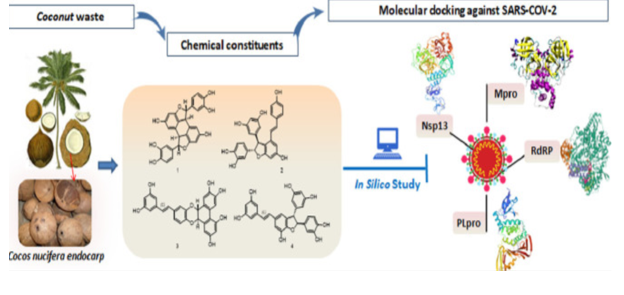
Natural compounds provide unlimited opportunities for new drug leads because of the unmatched availability of chemical diversity. However, there are still many species of plants that might possess a beneficial natural product that have still not been screened for medicinal use and might be a cause for a breakthrough in science. Therefore, more investigations should be done in various species of plants and other natural products. The analysis of bioactive compounds involving the applications of common phytochemical screening assays, chromatographic techniques and biological screening assays. Eleven compounds were isolated from the ethyl acetate extract of Cocos nucifera L endocarp, jezonofol 1, scirpusin A 2, cassigarol G 3, maackin A 4, threoguiacyl glycerol-8'-vanillic acid ether 5, erythroguiacyl glycerol-8'-vanillic acid ether 6, apigenin-7-O-β-D-glucoside 7, piceatannol 8, p-hydroxy-benzoic acid 9, protocatechuic acid 10 and vanillic acid 11. The isolated compounds were virtually screened against four critical components of severe acute respiratory syndrome corona virus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the main protease (Mpro), papain-like protease (PLpro), nonstructural protein 13 (nsp13) and RNA dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp). Particularly, compounds 1, 2 and 3, showed a promiscuity pattern binding to multiple targets of SARS-CoV-2 replication. The list of the compounds was considered herein forms a primer for clinical investigation in COVID-19 patients and directing for further antiviral examinations. |